-

Beyond Compost
Leafmould
If you have deciduous trees in your garden, you will be able to make leafmould – another useful material for the organic gardener. Making it is far simpler that composting and is just a matter of collecting all your fallen leaves in a heap and jumping up and down on them to exclude air and fit more in. Unlike compost, leaves decompose anaerobically, in other words without oxygen.
 It is a good idea to make a wire netting enclosure or something similar to prevent them blowing away. Leafmould is devoid of nutrients, but it is great to use as a soil conditioner, a peat substitute and as a mulch. Avoid adding evergreen leaves to the heap because they are very slow to rot down and many of them are quite toxic to other plants.
It is a good idea to make a wire netting enclosure or something similar to prevent them blowing away. Leafmould is devoid of nutrients, but it is great to use as a soil conditioner, a peat substitute and as a mulch. Avoid adding evergreen leaves to the heap because they are very slow to rot down and many of them are quite toxic to other plants.Green Manures
While compost is the primary way that an organic gardener adds fertility to the soil, there are other options too. Green manures such as mustard, clover and phacelia can be sown on any bare patch of ground to keep it covered and then dug in before the ground is planted to add structure and fertility.
Manure
 Well-rotted manure is good for hungry crops like potatoes, but be sure that it is obtained from a safe, ideally organic, source. There have been problems with manure contaminated with persistent pesticides causing problems for gardeners. Well-rotted is important too, if manure is too fresh it will actually deprive the soil of nitrogen
Well-rotted manure is good for hungry crops like potatoes, but be sure that it is obtained from a safe, ideally organic, source. There have been problems with manure contaminated with persistent pesticides causing problems for gardeners. Well-rotted is important too, if manure is too fresh it will actually deprive the soil of nitrogenWormeries
Where space is so limited that there is no room for compost bins, a wormery, properly managed, will produce modest quantities of both fertile compost and nutrient rich liquid feed.
Natural Fertilisers
Fish, blood and bone is a natural alternative to chemical fertilisers and is spread on the soil in a similar way. It is high in potash and is a useful boost if plants are failing to flower or fruit. Seaweed, either fresh or as a dried powder performs a similar function.
Liquid Feeds
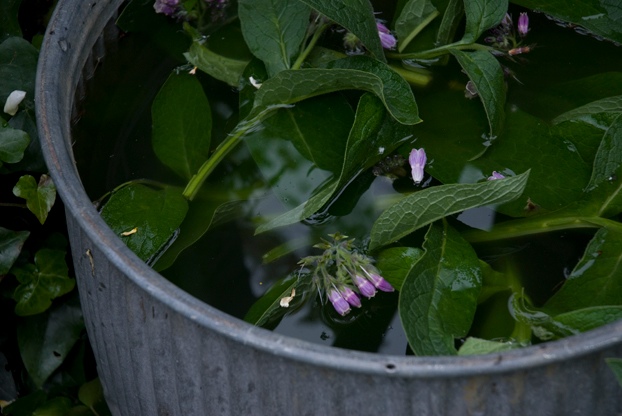
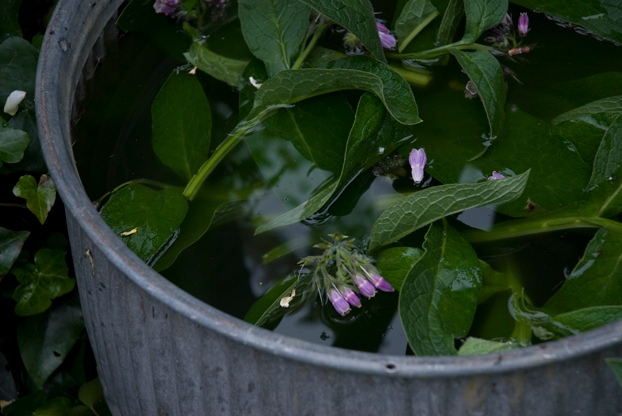
Although the organic gardener focuses mainly on improving the soil by the addition of compost for fertility and humus for better soil texture, there is also a role for liquid feeds, especially with vegetables and container grown plants. There are some good organic liquid feeds commercially available, but you can also make your own from comfrey. Use the Bocking 14 strain available from Garden Organic. Harvest the leaves four times during the growing season and steep them in enough water to cover all the leaves. The evil-smelling brew that results can added to your watering can at a 10% dilution. Keep the comfrey and water mix covered while it brews.